Compare and order fractions
Key notes:
Types of Fractions
- Like fractions: Same denominators (e.g., 3/8 and 5/8)
- Unlike fractions: Different denominators (e.g., 2/3 and 3/5)
Comparing Like Fractions
- Rule: Just compare numerators.
- Example:
3/8 < 5/8 because 3 < 5
Comparing Unlike Fractions
Method 1: Convert to Equivalent Fractions (Common Denominator)
- Find the LCM of denominators
- Convert both fractions to have the same denominator
- Then compare numerators
Example:
Compare 2/3 and 3/5
LCM of 3 and 5 = 15
2/3=10/15,3/5=9/15
10/15>9/15 → So, 2/3>3/5
Method 2: Cross Multiplication
- Multiply numerator of each fraction with the denominator of the other.
- Compare results.
Example:
Compare 23 and 35
Cross multiply:
2 × 5 = 10
3 × 3 = 9
Since 10 > 9, 2/3 > 3/5
Ordering Fractions
- Step 1: Convert all fractions to have the same denominator or use decimal conversion
- Step 2: Arrange based on numerators or decimal values
Example:
Order: 1/2 , 3/4 , 2/3
Convert to decimals:
1/2 = 0.5 , 3/4 = 0.75 , 2/3 ≈ 0.666
Ascending order: 1/2 < 2/3 < 3/4
Tips
- Always simplify fractions before comparing if needed.
- Use number lines for a visual understanding.
- For mixed numbers, convert to improper fractions if needed.
Learn with an example
🔥Which fraction is greater?
A} 1/10
B} 8/10
You can use models to compare fractions.
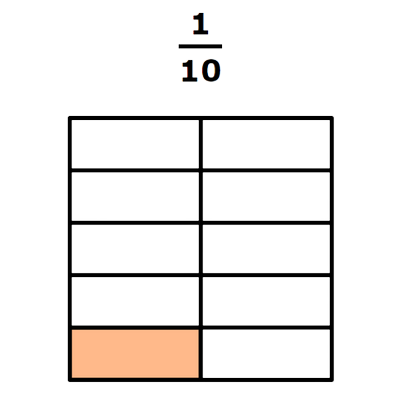
8/10
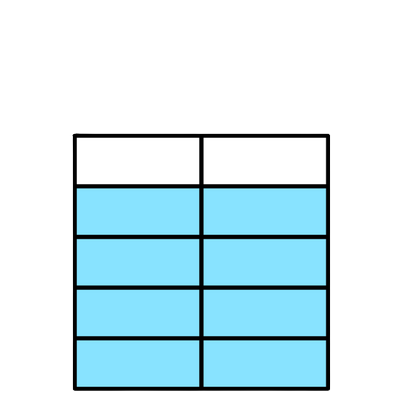
Both shapes have 10 equal parts and are the same size. So, the parts in the first shape are the same size as the parts in the second shape.
When parts are the same size, 8 parts is more than 1 part. So, more of the second shape is colored.
8/10 is greater than 1/10.
🔥Which fraction is less?
A} 1/4
B} 3/4
You can use models to compare fractions.
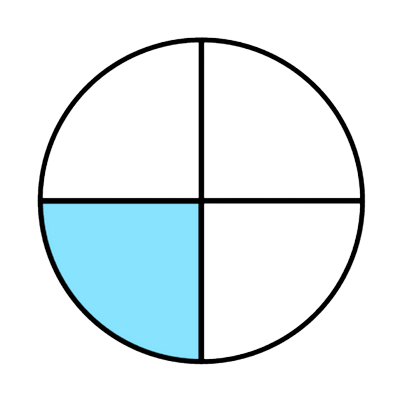
1/4
3/4
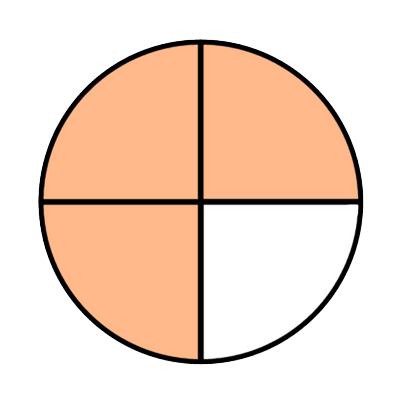
Both shapes have 4 equal parts and are the same size. So, the parts in the first shape are the same size as the parts in the second shape.
When parts are the same size, 1 part is less than 3 parts. So, less of the first shape is colored.
1/4 is less than 3/4.
🔥Which fraction is less?
A} 1/2
B} 1/12
You can use models to compare fractions.
1/2
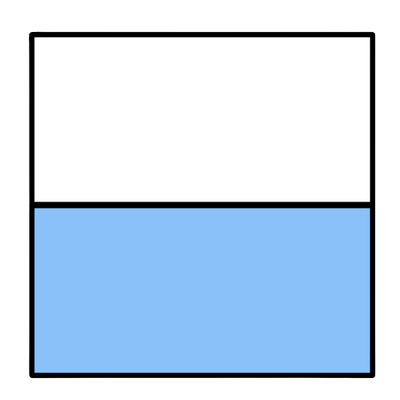
1/12
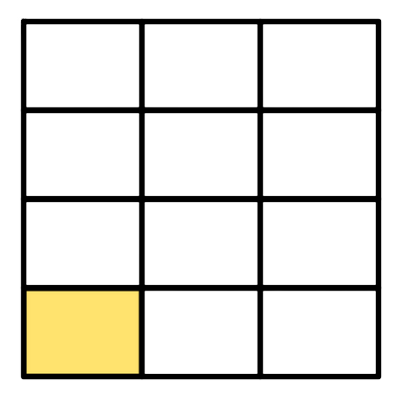
Both shapes have 1 colored part, but the part in the second shape is smaller. This is because the second shape is sliced into 12 parts, instead of 2.
So, less of the second shape is colored.
1/12 is less than 1/2.

Let’s practice!

