Digestion in Humans
digestion in human by Delta publications
Key Notes :
Definition of Digestion:
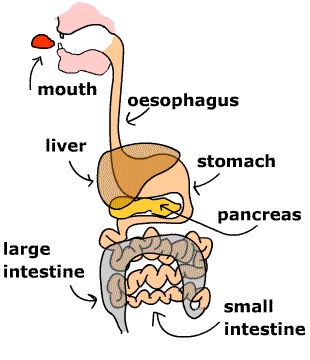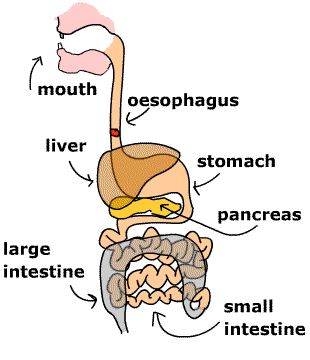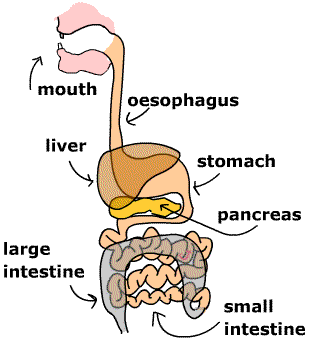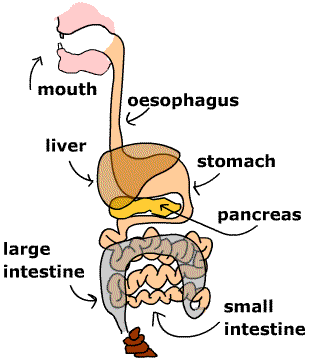
- Digestion is the process of breaking down food into simpler forms that the body can absorb and use for energy, growth, and repair.
Digestive System Components:

- Mouth: The digestion process begins here. Teeth break down food into smaller pieces, and saliva (containing the enzyme amylase) starts digesting starch.
- Esophagus: A muscular tube that transports food from the mouth to the stomach through peristalsis (wave-like muscle movements).
- Stomach: Produces gastric juices (containing hydrochloric acid and pepsin) to digest proteins. The acidic environment kills harmful bacteria.
- Small Intestine: The main site of digestion and absorption. Digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver help break down food.
- Large Intestine: Absorbs water and minerals. The undigested waste is prepared for elimination.
- Rectum and Anus: Store and eliminate solid waste from the body.
Role of Digestive Juices:

- Saliva: Begins carbohydrate digestion in the mouth.
- Gastric Juice: Aids protein digestion in the stomach.
- Bile: Produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder; helps emulsify fats in the small intestine.
- Pancreatic Juice: Contains enzymes that digest proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
- Intestinal Juice: Completes the digestion of food into absorbable molecules.
Enzymes in Digestion:

- Amylase: Breaks down carbohydrates into simple sugars.
- Pepsin: Digests proteins into smaller peptides.
- Lipase: Breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Absorption:
- Nutrients are absorbed in the small intestine via finger-like projections called villi. These increase the surface area for maximum absorption.
- Glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids enter the bloodstream or lymph for transport to cells.
Egestion:
- The removal of undigested and unabsorbed food material as feces through the anus.
Importance of a Balanced Diet:

- A balanced diet ensures all nutrients are available for proper digestion and absorption.
Common Digestive Disorders:
- Indigestion: Discomfort due to improper digestion.
- Acidity: Excess production of stomach acid.
- Constipation: Difficulty in passing stools due to low fiber intake or dehydration.
Tips for Healthy Digestion:
- Eat fiber-rich foods.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Avoid overeating and processed foods.
- Maintain regular meal times.
Let’s practice!

